Understanding Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: Insights and Innovations
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) is a hereditary disorder that affects the peripheral nerves, significantly impacting mobility and day-to-day functioning. As we delve into this complex condition, we’ll explore not only its symptoms and causes but also the latest innovations in treatment and management, particularly how advancements in AI and automation, like n8n workflows, can support those living with CMT.
What is Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease?
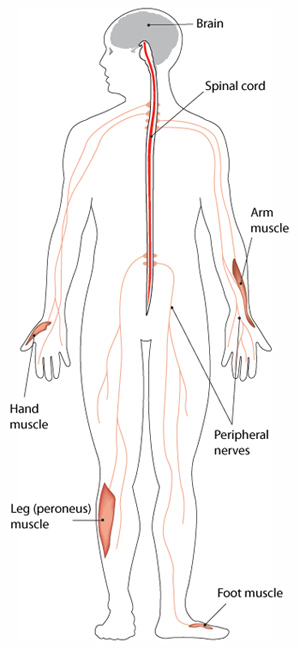
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is named after the three physicians who first described it in the late 19th century. It is the most common inherited neurological disorder, affecting approximately 1 in 2,500 people. CMT encompasses a range of inherited neuropathies that affect the myelin sheath or the axons of the nerves, leading to muscle weakness and atrophy, sensory loss, and various complications related to limb mobility.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The hallmark symptoms of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease typically emerge in childhood or early adulthood, though they can appear at any age. Common symptoms include:
- Muscle weakness, particularly in the feet and hands
- Loss of sensation or abnormal sensations in the limbs
- Foot deformities, such as high arches or hammertoes
- Difficulty walking and an increased risk of falls
- Muscle wasting, particularly in the lower legs
Diagnosis of CMT generally involves a comprehensive neurological examination, genetic testing, and certain electrodiagnostic studies to assess nerve function. To learn more about the diagnostic process, refer to the Cleveland Clinic.
Genetic Background and Variants of CMT
CMT is predominantly caused by genetic mutations that affect myelin or axonal function. The most prevalent genetic variants related to CMT include:
- CMT1A: Caused by a duplication of the PMP-22 gene, this form is the most common and leads to demyelination.
- CMT1B: This variant involves mutations in the MPZ gene, also resulting in demyelination.
- CMT2: This variant affects the axons and involves several subtypes of genetic abnormalities.
- CMTX: A form linked to mutations on the X chromosome, it primarily affects males but can also impact females.
Understanding which genetic variant a patient has is crucial for tailoring appropriate interventions and therapies.
Current Treatments and Management Strategies
While there is no cure for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, various treatments aim to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These include:
- Physical therapy: Helps maintain muscle strength and prevent contractures.
- Occupational therapy: Focuses on improving day-to-day activities and facilitating independence.
- Orthotic devices: Customized braces can improve mobility and provide support.
- Pain management: Medications may be prescribed to alleviate neuropathic pain.
Moreover, advancements in telemedicine enable healthcare providers to stay connected with patients and adjust treatment plans as necessary, improving patient engagement and compliance.
Innovations in AI and Automation for CMT Management
The intersection of healthcare and technology is revolutionizing how chronic conditions are managed. For Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, n8n workflows can be leveraged to automate various care processes, enhance data management, and improve communication between patients and healthcare providers.
One practical application is the creation of automated systems for appointment reminders, medication schedules, and symptom tracking. These workflows help to ensure that individuals with CMT adhere to their treatment regimens and from this, derive the maximum benefit from the healthcare resources available to them.
Furthermore, AI can assist in analyzing large datasets from clinical studies, enabling researchers to discover new therapeutic targets and potential breakthroughs in treatment modalities. Utilizing AI-driven tools can significantly accelerate research, making ways for more personalized approaches to managing CMT.
Psychosocial Impact of CMT
Living with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease extends beyond the physical symptoms, as individuals often experience significant psychosocial challenges. The chronic nature of the disease can lead to feelings of frustration, isolation, and anxiety. Addressing this aspect requires comprehensive care that includes mental health support.
Support groups can provide a community for individuals affected by CMT, allowing them to share experiences, coping strategies, and emotional support. Implementing digital platforms for these interactions can ensure wider accessibility and foster connections among patients.
Looking Ahead: Future Directions in CMT Research
The future of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease research is promising, with ongoing studies focusing on genetic therapies and novel pharmacological approaches. Emerging gene-editing technologies, like CRISPR, hold the potential to address some of the underlying genetic causes of CMT, possibly leading to curative strategies in the future.
Researchers are also exploring different therapeutic avenues, such as nerve growth factor therapy and small molecules that can enhance nerve regeneration. The integration of AI technologies in research and patient care will likely continue to evolve, bringing innovative solutions tailored to individual needs.
Conclusion
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is a complex condition that requires awareness, understanding, and proactive management to navigate its challenges. As healthcare continues to integrate advanced technologies like AI and automation into patient care, the potential to enhance the lives of individuals with CMT becomes increasingly achievable. Ongoing research and community support will remain integral as we explore new frontiers in understanding and treating this hereditary neuropathy.
For more comprehensive information on Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, please visit the Cleveland Clinic.