Understanding DNA: The Key to Unlocking Genetic Mysteries
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is often described as the blueprint of life. It contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive, and reproduce. This article delves into the fascinating world of DNA, exploring its structure, function, and significance in genetic studies.
What is DNA?
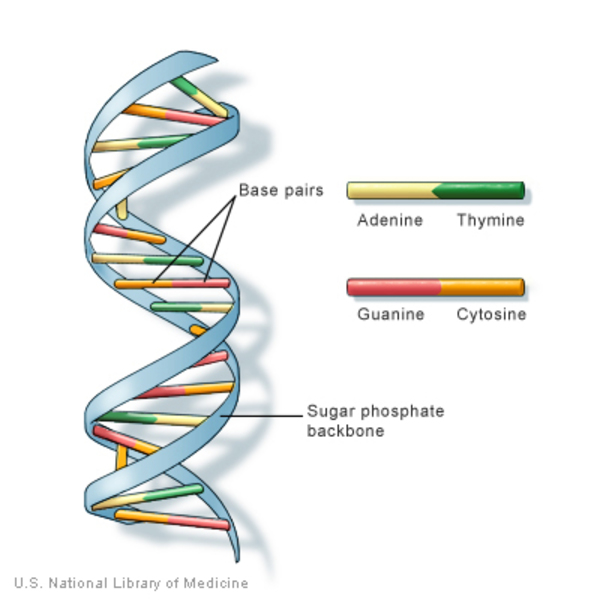
At its core, DNA is a molecule composed of two strands that coil around each other to form a double helix. Each strand is made up of a sequence of nucleotides, which are the basic building blocks of DNA. These nucleotides consist of a phosphate group, a sugar molecule, and a nitrogenous base. The four types of nitrogenous bases—adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G)—pair specifically (A with T, C with G) to form the rungs of the DNA ladder.
The Structure of DNA
Understanding the structure of DNA is fundamental to comprehending how it functions. The double helix was first described by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953. Their discovery shed light on how genetic information is stored, replicated, and transmitted across generations. The specific sequence of nucleotides in DNA is what encodes genetic information, determining everything from physical traits to susceptibility to certain diseases.
The Function of DNA
DNA serves various crucial roles in biological systems:
- Genetic Information Storage: DNA stores genetic information that guides the development and functioning of living organisms.
- Replication: Before a cell divides, it composes a copy of its DNA, which is essential for cell division and the propagation of genetic material.
- Protein Synthesis: DNA provides the instructions for synthesizing proteins through a process that involves transcription and translation.
The Importance of DNA in Genetics
DNA plays a pivotal role in genetics, informing how traits are inherited from parents to offspring. Understanding genetic inheritance patterns allows scientists and clinicians to predict genetic disorders and tailor medical treatments accordingly. For example, advances in personalized medicine rely heavily on genetic information derived from DNA to optimize therapeutic strategies for individual patients.
Applications of DNA Technology
The implications of DNA research and technology are vast, affecting numerous fields:
- Forensic Science: DNA profiling has revolutionized forensic investigations, allowing for the accurate identification of individuals involved in criminal cases.
- Gene Therapy: Techniques such as CRISPR-Cas9 have emerged, enabling scientists to edit genes within living organisms to treat genetic diseases.
- Biotechnology: DNA technology is integral to genetic engineering, leading to advancements in agriculture, such as genetically modified organisms (GMOs) that can withstand pests and environmental stresses.
Considerations and Ethical Implications of DNA Research
While the advancements in DNA technology are promising, they also raise ethical considerations. Issues such as privacy, consent, and the potential for genetic discrimination are paramount in discussions about genetic testing and manipulation. The responsible use of genetic information is critical as we move forward in this rapidly evolving field.
Conclusion
DNA is a remarkable molecule that serves as the foundation of life. Its exploration has led to groundbreaking discoveries in genetics and has transformed our approach to medicine, law, and biotechnology. As we continue to unlock the secrets of DNA, it is crucial to navigate the ethical landscape carefully, ensuring that the benefits of our discoveries are realized responsibly and equitably.
For more detailed information, visit MedlinePlus – Understanding DNA.