Understanding DNA: The Blueprint of Life
Deoxyribonucleic acid, commonly known as DNA, is the fundamental building block of life. As a crucial molecule that carries genetic instructions essential for the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses, understanding DNA is imperative for HR professionals and business leaders alike, especially in fields like genetic testing, biotechnology, and healthcare.
What is DNA?
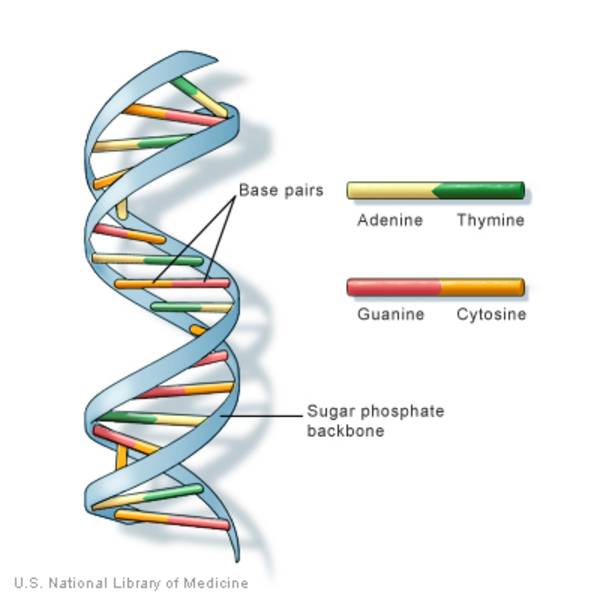
DNA is a double-stranded molecule composed of nucleotides, each consisting of a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), and a nitrogen base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine). The unique sequence of these bases encodes genetic information, much like letters in a sentence. The structure of DNA was famously discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick, who described its double helix formation in 1953. This structure not only allows for the compact storage of genetic information but also facilitates replication and transcription, crucial processes for all living organisms.
The Significance of DNA in Modern Science
Understanding DNA goes beyond academic interest; it plays a pivotal role in various sectors, including healthcare, agriculture, and forensic science. From genetic testing that aids in diagnosing hereditary conditions to advancements in CRISPR technology for gene editing, DNA research is at the forefront of scientific development.
1. Healthcare Applications
In healthcare, DNA analysis is revolutionizing how we approach diseases. Genetic testing can identify predispositions to diseases such as cancer and offer personalized treatment plans. Companies that specialize in genetic testing are growing rapidly, providing insights into patients’ health that were previously unavailable. This demand for genetic information is leading to a shift in how healthcare is delivered, emphasizing preventive care and personalized medicine.
2. Agriculture Innovations
The role of DNA extends to agriculture, where genetic modification allows for the development of crops that are resistant to pests and diseases. This not only increases yield but also minimizes the need for chemical pesticides, promoting sustainable farming practices. Understanding the genetic makeup of plants enables breeders to select traits that enhance productivity and address food security challenges.
3. Forensic Science
In forensic science, DNA profiling is an essential tool for criminal investigations. By analyzing an individual’s DNA, law enforcement can identify suspects or victims with remarkable accuracy. This technique has transformed the way crimes are solved and has led to the exoneration of wrongly convicted individuals.
The Future of DNA Research and its Implication for Business
As we move into an era where DNA technology continues to advance, businesses that leverage this information stand to benefit significantly. HR professionals and business leaders must understand the implications of DNA applications in their industries:
1. Ethical Considerations
With the power of DNA comes the responsibility to handle genetic information ethically. Companies must develop clear guidelines for privacy and data protection to maintain trust with consumers and employees. The implications of DNA data misuse can be severe, leading to discrimination and breaches of privacy.
2. Talent Acquisition and Employee Health
HR professionals can utilize genetic insights to design more effective wellness programs that consider employees’ unique genetic predispositions. This personalized approach can improve workplace health and productivity. Moreover, understanding the genetic factors affecting health and performance can assist in talent acquisition, ensuring a better fit between candidates and roles.
3. Innovation and Competitive Advantage
Companies that prioritize DNA research and its applications can gain a competitive edge. Collaborations with biotech firms and research institutions can lead to innovative products and services that meet the evolving demands of consumers. Staying ahead of the trends in DNA research will position businesses as leaders in their fields.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DNA is more than just a scientific curiosity; it is a key driver in healthcare, agriculture, and criminal justice that has profound implications for business leaders and HR professionals. As research evolves, the understanding and application of DNA will become increasingly relevant across industries. Organizations that remain informed and adaptable to these changes will not only enhance their operational efficacy but will also contribute to a broader understanding of human health and behavior.
For further exploration into the basics of DNA, visit the MedlinePlus Genetics website.